How to Find Retained Earnings: A Simple Guide for 2025 Success
Understanding how to find retained earnings is essential for business owners and investors alike. Retained earnings represent the cumulative amount of net income that companies retain for reinvestment, payment of debt, or other reinvestment strategies, rather than distributing it to shareholders as dividends. In this guide, we’ll explore the retained earnings calculation, the retained earnings formula, examples, how to increase retained earnings, and much more, providing you with the insights needed to harness this powerful financial metric for your success in 2025.
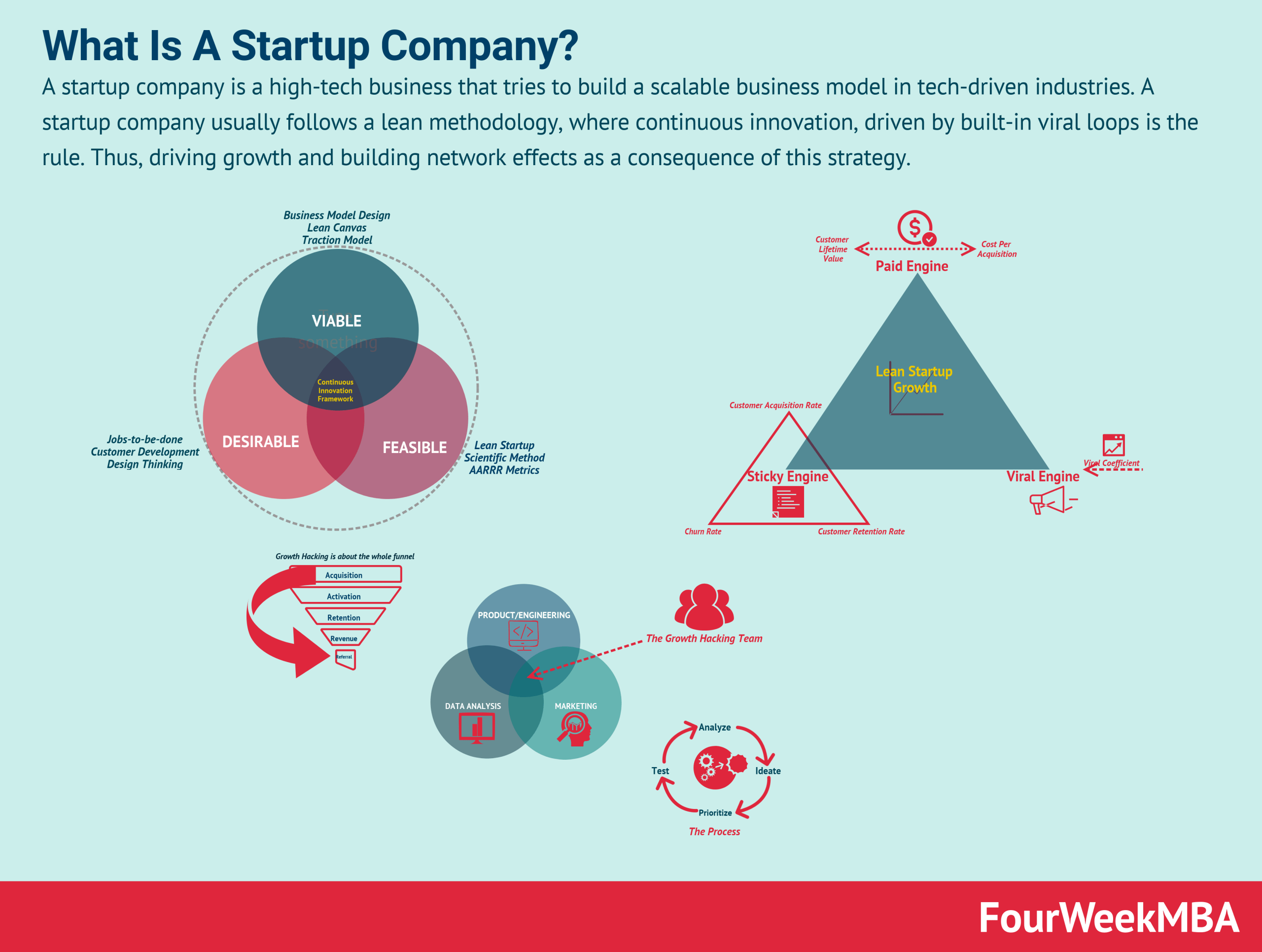
Understanding Retained Earnings
Retained earnings, often considered the lifeblood of a business, indicate how much profit a firm retains after paying dividends to its shareholders. This account has significant implications on the balance sheet, showcasing how effectively a company can reinvest its earnings for growth. Understanding the retained earnings definition and its importance is crucial for evaluating financial health and making informed decisions in any organization. Investors often look at retained earnings as a way to gauge a company’s ability to grow, distribute dividends in the future, and manage financial performance over time.
Retained Earnings Definition and Meaning
The retained earnings definition refers to the profits that a company has reinvested in its operations instead of distributing it to shareholders as dividends. On a company’s balance sheet, retained earnings are cumulative and reflect the total net income retained from the company’s inception, minus any dividends declared. For example, a tech startup may choose to allocate most of its earnings to develop new products and services rather than distribute them immediately to shareholders. This retention strategy emphasizes growth, which could potentially lead to higher equity values in the long term.
Importance of Retained Earnings in Business
The importance of retained earnings cannot be overstated. It serves as a critical indicator of a company’s financial health and sustainability. Well-managed retained earnings can provide firms with the necessary capital to invest in expansion opportunities like new projects, enhancing technology, and enriching workforce talent. Furthermore, positive growth in retained earnings signals to investors that the company is effectively generating more income than it is distributing, which can positively impact stock price and company valuation.
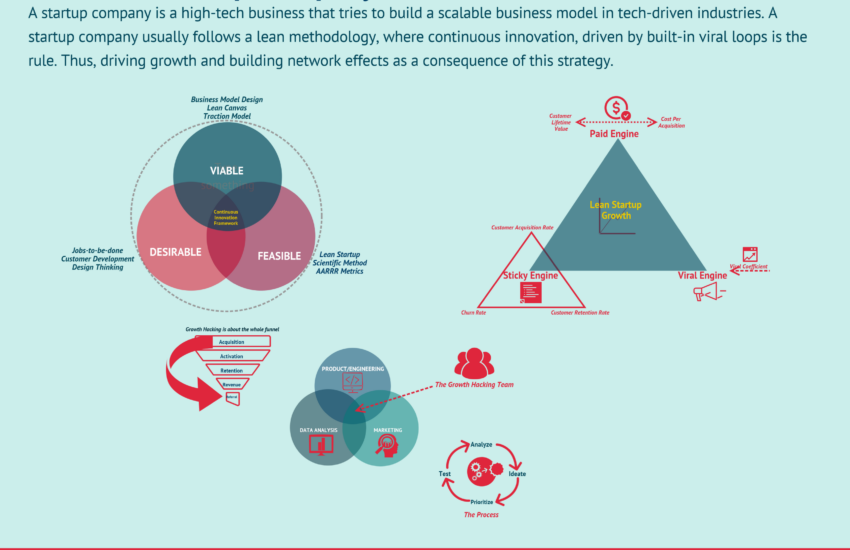
Calculating Retained Earnings
Calculating retained earnings involves a simple formula, where you start with the previous year’s retained earnings balance, add the net income from the current year, and subtract any dividends paid out. The retained earnings formula can be expressed as follows:
Retained Earnings = Previous Retained Earnings + Net Income – Dividends Paid
This straightforward calculation allows firms to track retained earnings through an easy annual review. For instance, if a company had a retained earnings balance of $50,000 at the beginning of the year, earned $20,000 in net income, and paid out $5,000 in dividends, the retained earnings at the end of the year would total $65,000.
How to Increase Retained Earnings
Increasing retained earnings is vital for a company’s growth trajectory and overall financial stability. There are several strategies that organizations can employ to achieve this, from maximizing profits to minimizing dividend payouts. Understanding retained earnings management is crucial for small businesses looking to firmly ground themselves in a competitive marketplace.
Retained Earnings Growth Strategies
One effective approach to increase retained earnings is by implementing various retained earnings growth strategies. This may include cost-cutting measures, improving operational efficiencies, and optimizing pricing strategies. For example, a manufacturing company can bolster its retained earnings by streamlining production operations which lowers costs and subsequently increases profit margins. These profits can then be fed back into the business instead of being distributed as dividends.
Retained Earnings and Dividends
Understanding the connection between retained earnings and dividends is also fundamental. Decisions regarding how much of the company’s net income is distributed as dividends versus how much is reinvested affect the retained earnings balance. Companies that choose to reinvest profits into growth opportunities rather than pay out substantial dividends tend to see larger increases in their retained earnings over time. It’s a balancing act that is particularly important for effective financial planning and retained earnings assessment.
Importance of Managing Retained Earnings
Effective retained earnings management plays a critical role in ensuring the longevity and sustainability of a business. By regularly analyzing retained earnings, companies can adjust their strategies according to market conditions, reinvest in innovation, and prepare for future challenges. This can include creating financial forecasts based not only on retained earnings but on their overall strategic goals. Well-informed decisions can ultimately lead to increased shareholder value and business expansion.
Retained Earnings in Financial Statements
Retained earnings are prominently featured in financial statements, particularly the balance sheet and statement of changes in equity. In understanding retained earnings in these contexts, stakeholders can gauge a company’s profitability, financial history, and future potential effectively. Analyses of retained earnings reporting enhance transparency and enable better decision-making for investments.
Retained Earnings on the Balance Sheet
On the balance sheet, retained earnings appear under the equity section and are cumulatively updated as profits or losses are recorded. A growing retained earnings figure is generally seen as a sign of a company’s solid growth and profitability, while stagnant or decreasing amounts may raise red flags for investors regarding potential inefficiencies or weakening business viability. This representation allows stakeholders to grasp the firm’s profit allocation choices quickly.
Retained Earnings Report and Analysis
The retained earnings report is not just an isolated number; it’s tied to many financial outcomes, such as dividend policies and additional funding for business endeavors. Financial analysts frequently leverage these insights for retained earnings analysis, providing feedback to organizations about their financial strategies and performance tracking. For instance, companies may resort to year-over-year retention analysis to establish trends and make informed forecasts about future earnings allocations.
Retained Earnings Implication for Investors
Investors pay close attention to retained earnings when evaluating a company’s potential growth, stability, and dividend policies. Understanding retained earnings insights not only aids in assessing performance but also offers essential indicators regarding future investment returns. By utilizing rich data resources such as retained earnings trends and patterns, investors can make sound judgements about where to allocate their capital, guiding decisions about future engagements or disbursals.
Key Takeaways
- Retained earnings represent the accumulated profits a company reinvests rather than pays out as dividends.
- Understanding how to calculate retained earnings is essential for assessing financial performance.
- Implementing effective retained earnings management and growth strategies is vital for long-term stability.
- Retained earnings play a crucial role in financial statements, influencing investment decisions.
- Continual analysis and reporting of retained earnings can provide critical insights for both management and investors.
FAQ
1. What is the importance of retained earnings for small businesses?
Retained earnings provide small businesses with necessary capital for growth and development. They enable reinvestment in operations, product development, or market expansion. By maintaining healthy retained earnings, small businesses can ensure financial stability, which is vital for maneuvering through fluctuating market conditions.
2. How do retained earnings impact financial planning?
Retained earnings directly influence a company’s financing strategy and budget planning. When planning for the future, businesses assess their retained earnings to determine funding sources for expansion or to build reserves for emergencies. This financial flexibility enables a company to stabilize cash flow and supports overall strategic objectives.
3. How can companies effectively report retained earnings?
Companies can effectively report retained earnings by providing clear and detailed disclosures in their financial statements. This can include a breakdown of how retained earnings have changed over time, enabling stakeholders to understand earnings utilization and assess business strategies. Financial transparency fosters trust and promotes informed decision-making among investors.
4. What strategies can increase retained earnings?
To increase retained earnings, companies can focus on strategies such as minimizing dividend payouts, enhancing operational efficiencies, and adopting cost-effective measures of accounting for retained earnings. Additionally, generating more revenue through market expansion or by enhancing product offerings can contribute significantly to the growth of retained earnings over time.
5. How does retained earnings affect shareholder value?
Retained earnings impact shareholder value as they reflect a company’s profitability and efficiency in utilizing income for growth instead of distributing it entirely as dividends. Higher retained earnings can lead to increased valuation and positive perception among investors, thus enhancing overall shareholder value.