Master Synthetic Division: Effective Techniques to Succeed in 2025
Simplifying Polynomial Division with Synthetic Division
Synthetic division is an **efficient method** for dividing polynomials, especially when dealing with linear divisors. Unlike long division, this technique significantly reduces calculation time and complexity. To master synthetic division, it helps to understand its foundational elements: **numerator**, **divisor**, and **coefficients**. This method streamlines dividing polynomials, making the process more intuitive. For example, if you’re trying to find the quotient and remainder of \( P(x) = x^3 + 2x^2 – 5x + 6 \) when divided by \( x – 2 \), synthetic division simplifies this process remarkably. Remember that, during the process, you are primarily manipulating the **coefficients** of the polynomial.
Understanding the Steps of Synthetic Division
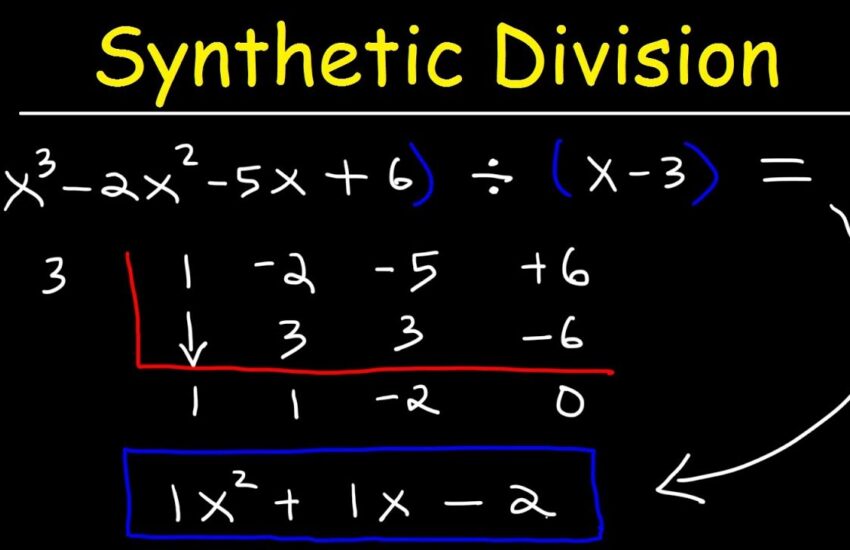
To apply the synthetic division method effectively, you must follow the steps of synthetic division carefully. Begin by writing down the coefficients of the polynomial you are dividing. Following this, draw a vertical bar with the root of the divisor (like \( r \) when dividing by \( x – r \)) to the left. Multiply the root by the current leading coefficient, then add it to the next coefficient. Repeat this process for each coefficient until you’ve processed them all. The final set of numbers represents the coefficients of the quotient polynomial, while the last number is the **remainder**. Engaging in practice problems, particularly **synthetic division examples**, will solidify your understanding of this process and help you excel in polynomial functions.
Applying the Synthetic Division Formula
The **synthetic division formula** condenses what can be a complex procedure into an accessible format. If the polynomial \( P(x) \) is expressed as \( ax^n + bx^{n-1} + … + c \), where you are dividing by \( x – r \), the formula will systematically guide you through each calculation. Notably, the method applies not just to standard polynomials but also extends its utility to **complex polynomials** and various cases of polynomials such as **quadratic** and **cubic** equations. When you grasp how to set up these equations properly, you’ll find solving them substantially easier and more systematic. This knowledge acts as a significant advantage when approaching polynomial equations in academic or practical contexts.
Understanding the Remainder Theorem
The **remainder theorem** is a vital tool in mastering synthetic division. It states that if a polynomial \( P(x) \) is divided by \( x – r \), the remainder of this division is \( P(r) \). Thus, by employing synthetic division, you’re not only dividing **algebraic expressions** but also can quickly check for the roots of polynomial functions. Incorporating this theorem into your learning routine enhances your effectiveness in determining factors of various polynomial identities. Efficiently evaluating several roots can significantly reduce the polynomial degree you’re working with, making your calculations faster and simpler.
Using Synthetic Division to Find Polynomial Roots
Finding the roots of a polynomial is straightforward with synthetic division, especially when relying on the remainder theorem. For instance, if we seek to determine the polynomial roots of a cubic function such as \( x^3 – 4x^2 + 3x – 12 \), we can implement **rational root** testing alongside synthetic division to locate possible solutions. Begin testing roots such as 1, -1, 2, etc., through synthetic division. If you discover that one of these roots directly equates the **remainder** to zero, you have successfully identified a factor of the polynomial. By iteratively applying synthetic division, we can systematically discover all roots of the polynomial.
Practical Applications of Synthetic Division
Synthetic division is not solely an academic exercise; it has real-world applications across various scientific and engineering contexts. From determining polynomial fitting in data sets to optimizing functions in design models, understanding **polynomial coefficients** and manipulating them through synthetic division is invaluable. Additionally, utilizing tools available like **synthetic division calculators** can assist in quickly checking your results against theoretical calculations. Simulating **complex numbers in polynomials** further emphasizes the necessity of honing your skills in this technique as polynomials underlie many applications, from statistical analysis to graphical representations in complex algebra.
Engaging Techniques to Master Synthetic Division
To develop proficiency in synthetic division, utilize engaging techniques that enhance your understanding. Start with interactive tools available online that offer visual representations of the synthetic division process. Create a series of practice problems, ranging from basic to more complex polynomials, and make an effort to solve them systematically. Furthermore, participating in study groups where you can teach your peers synthetic division methods reinforces your understanding. Combining different learning approaches enhances your skills in polynomial manipulation, effectively preparing you for various algebraic challenges.
Visualizing Synthetic Division for Better Understanding
Visually representing polynomial division can aid many learners. Draw diagrams illustrating the synthetic division process, depicting each step to visualize how coefficients are manipulated as the division progresses. Supplement this with the provided images to grasp the practical aspects of synthetic division. This visualization engages various learning styles and can solidify your understanding of the underlying math principles, promoting long-term retention of synthetic division concepts.
Overcoming Challenges in Synthetic Division
Many learners encounter difficulties when mastering the synthetic division method, often due to missteps in retaining the coefficients or misunderstanding the multiplication and addition sequences during the division. A great practice is to evaluate common pitfalls in academic resources, work with comprehensive workbooks, and focus on synthetic division exercises tailored to beginner and advanced learners. Encouraging a hands-on approach to learning aids in overcoming these challenges, making you more adept and confident in dealing with polynomial equations and algebraic expressions.
Key Takeaways
- Synthetic division simplifies the polynomial division process, making it essential for factoring and solving polynomial equations.
- Understanding the steps of synthetic division allows efficient manipulation of polynomial coefficients.
- The remainder theorem is a powerful tool in root finding and polynomial factorization.
- Real-world applications highlight the importance of synthetic division in science and engineering.
- Visual aids and interactive learning tools enhance understanding and mastery of synthetic division concepts.
FAQ
1. What are the primary steps of synthetic division?
The primary steps of synthetic division include writing down the coefficients of the polynomial, placing the divisor’s root to the left, and then following a multiplication and addition process for each coefficient. This allows for computing the quotient and remainder efficiently.
2. How does synthetic division relate to the remainder theorem?
The remainder theorem states that the remainder of a polynomial \( P(x) \) divided by \( x – r \) is equal to \( P(r) \). Thus, synthetic division directly applies, as the final output from the synthetic process reveals the remainder when you input the divisor’s root.
3. Can synthetic division be used for polynomials of degree higher than three?
Yes, synthetic division is versatile and can be used for polynomials of any degree, as long as the divisor is a linear polynomial of the form \( x – r \). The method effectively shortens computation time regardless of the polynomial’s degree.
4. What common mistakes should I avoid while using synthetic division?
Common mistakes include incorrectly ordering coefficients and misapplying addition and multiplication steps. It’s crucial to accurately manage coefficients throughout the calculation and to double-check each arithmetic operation to ensure accuracy.
5. How can I improve my synthetic division skills effectively?
Improving your skills can be practiced through various methods, including solving synthetic division exercises, limited-time quizzes, engaging in interactive online simulations, and working through tutorial videos that break down complex examples into manageable parts.
6. Is synthetic division faster than long division for polynomials?
Yes, synthetic division is typically faster than long division due to fewer steps involved in computing the quotient and remainder, making it a preferred method particularly for linear divisors.
7. What resources can help me practice synthetic division?
Resources include online tools and calculators specifically designed for synthetic division practice, comprehensive workbooks, educational websites focused on algebra instruction, and tutoring sessions that emphasize hands-on learning experiences.