Discover How to Find the Volume of a Triangular Prism
Understanding how to find the volume of a triangular prism is essential in geometry, as it lays the foundation for comprehending more complex three-dimensional shapes. This guide will walk you through the process using a triangular prism formula, ensuring you can calculate the volume of a triangular prism accurately and effectively in 2025. We will explore practical application, step-by-step calculations, and examples, making this guide both educational and practical for students and professionals alike.
Understanding the Triangular Prism Volume Formula
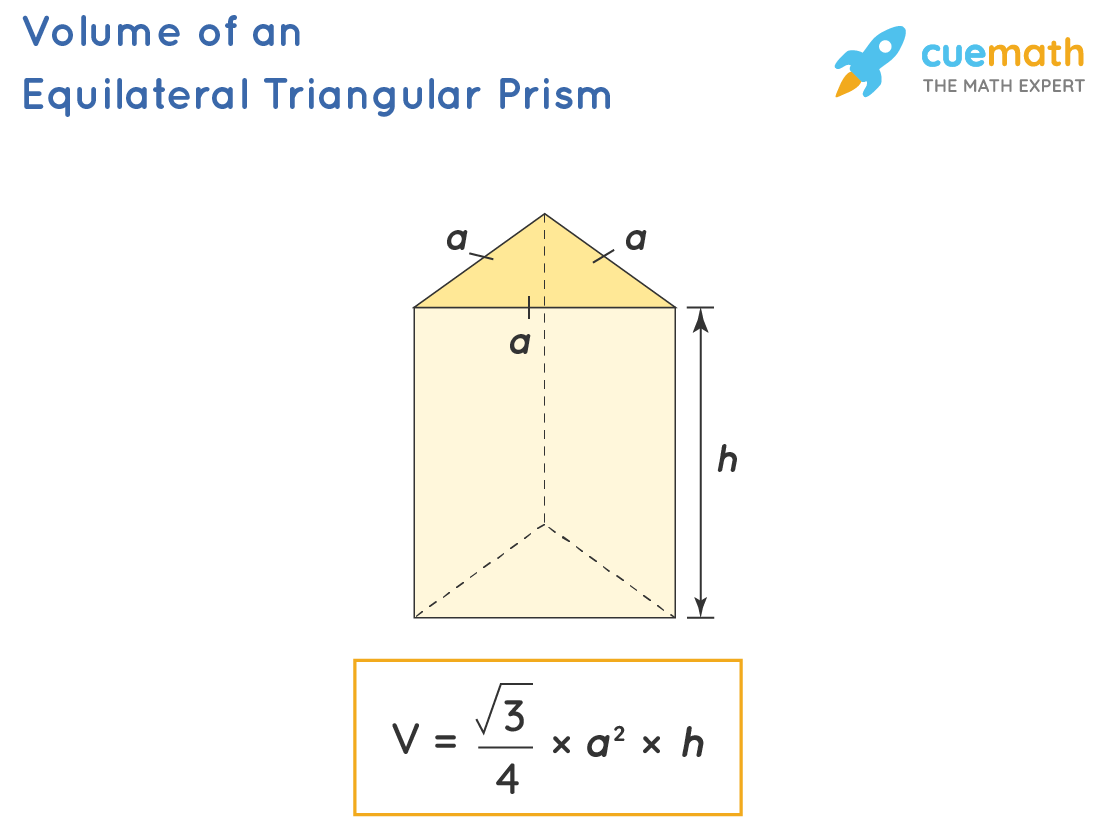
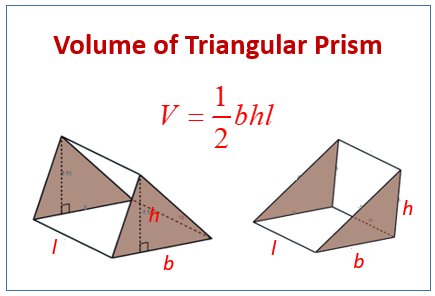
The first step in calculating the volume of a triangular prism is to understand the triangular prism volume formula. This formula is derived from its geometric properties and includes both the base area and the height of the prism. To simplify, the volume (V) of a triangular prism can be expressed as:
V = Base Area × Height
The base area is the area of the triangular face of the prism, which can be further calculated using the formula Area = 1/2 × base length × base height. Meanwhile, the height of the triangular prism refers to the perpendicular distance between the two triangular bases. Understanding this fundamental relationship is crucial when calculating the volume of solids in geometry.
Calculating the Base Area
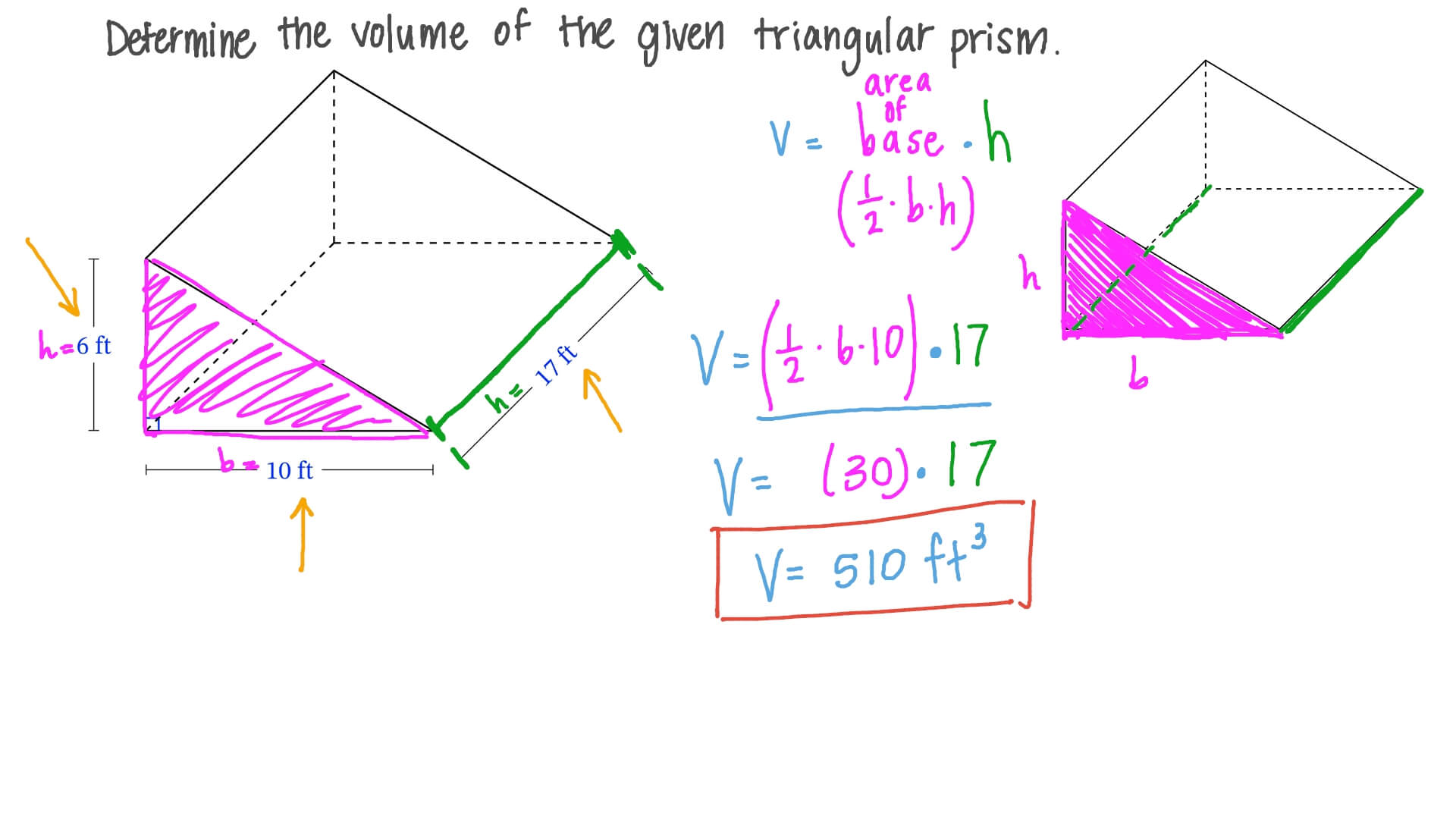
To find the volume of a triangular prism, one must first calculate the triangular prism base area. Let’s assume we have a triangular base with a base length (b) and a base height (h). Using the formula:
Area = 1/2 × b × h
For example, if the base length is 6 cm and the base height is 4 cm, the base area would be:
Area = 1/2 × 6 × 4 = 12 cm²
This gives us the base area which will be multiplied by the height of the prism to find the volume calculation.
Height and Volume Relationship
The height of a triangular prism significantly affects its volume in geometry. If we denote the height of the prism in our example as 10 cm, the volume can be calculated as follows:
V = Base Area × Height = 12 cm² × 10 cm = 120 cm³
This calculated volume indicates the space the prism occupies and is measured in cubic units. This relationship emphasizes how critical both the base area and the height are to the overall volume.
Simplifying Volume Calculation Techniques
When it comes to calculating the volume of a triangular prism efficiently, employing various techniques makes the process quicker and more intuitive. Using visualization, such as diagrams or 3D models can help students grasp these concepts more dynamically. Incorporating successful educational tools—like math software or mobile applications that depict triangular shapes in real life—can enrich the learning experience. Additionally, using the triangular prism property of symmetry can make it easier to understand how to dissect complex shapes into simpler ones to facilitate easier calculations.
Examples of Triangular Prisms in Real Life
Triangular prisms are not merely abstract concepts; they exist in various real-world applications. From architectural designs to engineering components, the practical use of triangular prisms spans numerous fields. Ingenuity in design often stems from principles found in geometry, where the stability offered by triangular forms is utilized.
Triangular Prism in Architecture
In architecture, triangular prisms create aesthetically pleasing and stable structures. Notably, roofs often adopt a triangular prism shape for enhanced durability and greater resistance to weather pressures. The geometric integrity provided by the triangular prism aligns with efficient energy use in buildings, thus underscoring the relevance of understanding their properties.
Triangular Prism in Engineering
Engineers frequently employ triangular prisms in their designs for bridges and other infrastructures. The rigidity of triangles helps in distributing weight evenly and providing strength while allowing for creative freedom in design. Mastery of the triangular prism volume helps engineers calculate material requirements more accurately and efficiently.
Right vs. Oblique Triangular Prisms
Understanding the differences between right and oblique triangular prisms is vital in geometry. A **right triangular prism** has its triangular bases directly aligned vertically, whereas an **oblique triangular prism** slants at an angle. Despite their differences, calculating the volume remains consistent across types—calculated with the same triangular prism volume formula but requiring an understanding of the specific dimensions involved. This insight can lend itself to enhanced spatial reasoning.
Practical Uses of Triangular Prism in Learning
In academic settings, learning through geometrical shapes often involves exploring triangular prism activities. Engaging with triangular shapes through experiential learning stimulates student interest and enhances understanding. Integrating models allows students to see and calculate volumes in a hands-on manner, transforming abstract theories into concrete knowledge.
Using Interactive Volumetric Tools
Many digital platforms offer interactive geometry tools to calculate volumes easily. These volumetric measurement tools allow learners to alter dimensions dynamically and observe how changes affect dimensions and volume. Focusing on practical measurement techniques using these tools actively engages students—a method better than traditional worksheet exercises.
Experimental Geometry Initiatives
Implementing classroom projects focusing on the physics of triangular prism shapes illustrates the impact of volume measurement. Experiments can include water filling triangular prism-shaped containers or measuring displacement to find volume in real-time, marrying theory with practical applications.
Innovative Teaching Methods for Volume
In workshops or community centers, students of all ages can benefit from innovative teaching methods that focus on tutorials about the importance of shapes in mathematics and how they apply to both everyday activities and complex designs. Leveraging technology not only enhances learning but also prepares students for future precise measurements needed in various disciplines aligned with volume measurement techniques.
Key Takeaways
1. The volume of a triangular prism can be efficiently calculated using its base area and height.
2. Understanding triangular prism properties aids in real-world application in engineering and architecture.
3. Engaging, hands-on learning promotes comprehension of volume calculations through experiential methods.
4. Utilizing interactive tools equips learners to visualize and measure volumes dynamically.
5. Exploring innovative teaching techniques enhances appreciation for geometry’s intertwining with real-life applications.
FAQ
1. What is the formula to find the volume of a triangular prism?
The volume of a triangular prism is calculated using the formula V = Base Area × Height. To find base area, use the formula Area = 1/2 × base length × base height.
2. How do you determine the base area of a triangular prism?
The base area can be determined by plugging the base length and base height into the area formula. Simply calculate Area = 1/2 × base length × base height for the triangular face of the prism.
3. What are the units used in measuring volume?
Volume is typically measured in cubic units, which represents the space occupied by the object. Common units include cubic centimeters (cm³) and cubic meters (m³).
4. Are there different types of triangular prisms?
Yes, triangular prisms can be categorized as right triangular prisms—where triangular bases are vertically aligned, or oblique triangular prisms—where bases are slanted.
5. How do triangular prisms differ from rectangular prisms?
Triangular prisms have triangular faces, while rectangular prisms feature rectangular bases. The volume calculation approaches can differ due to their geometric properties.
6. What’s an example of a real-life triangular prism?
Triangular prisms are often seen in the architectural design of roofs, where they provide stability and enhance aesthetic appeal through their geometric properties.
7. How can technology enhance understanding of triangular prisms?
Digital tools and applications allow students to visualize and manipulate triangular prism shapes dynamically, facilitating better comprehension of volume and spatial dimensions.